Most-read are based on citations from 2024 ~ 2026.
Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

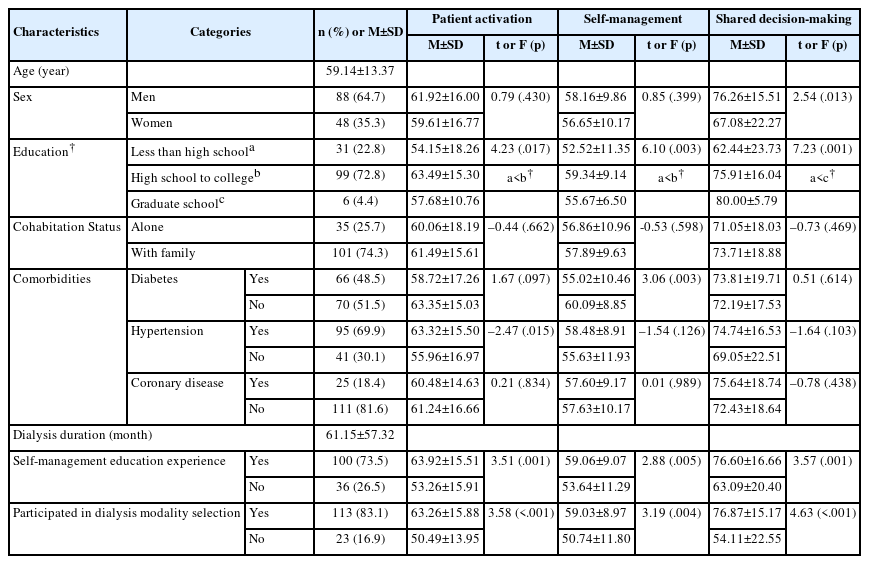
Citations

Citations

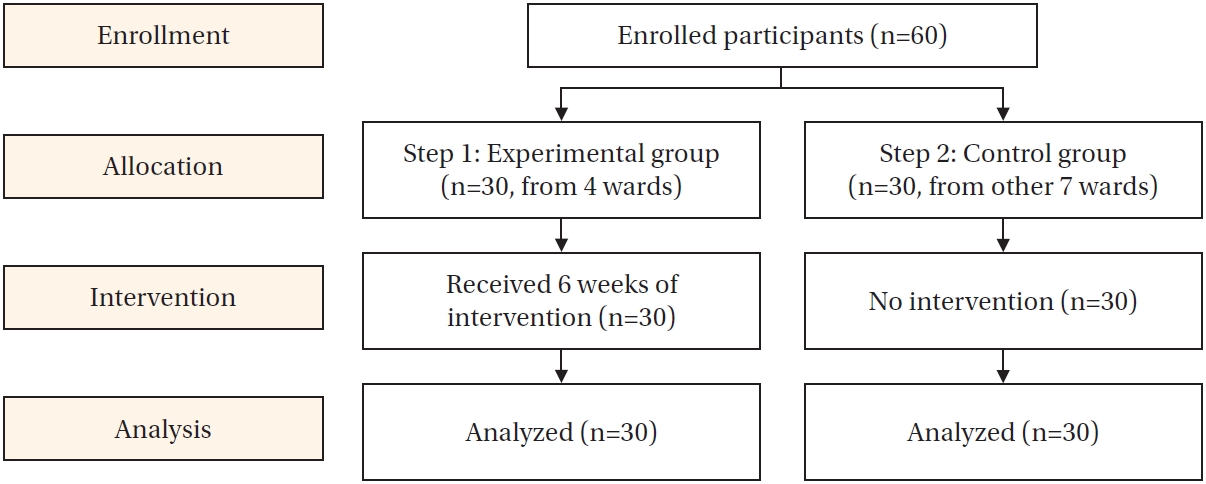
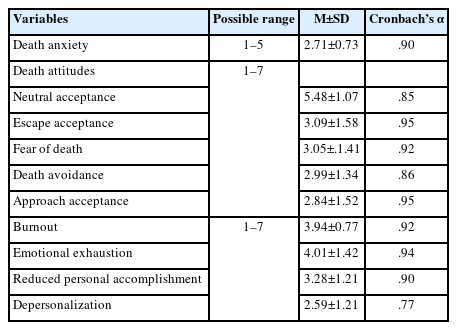
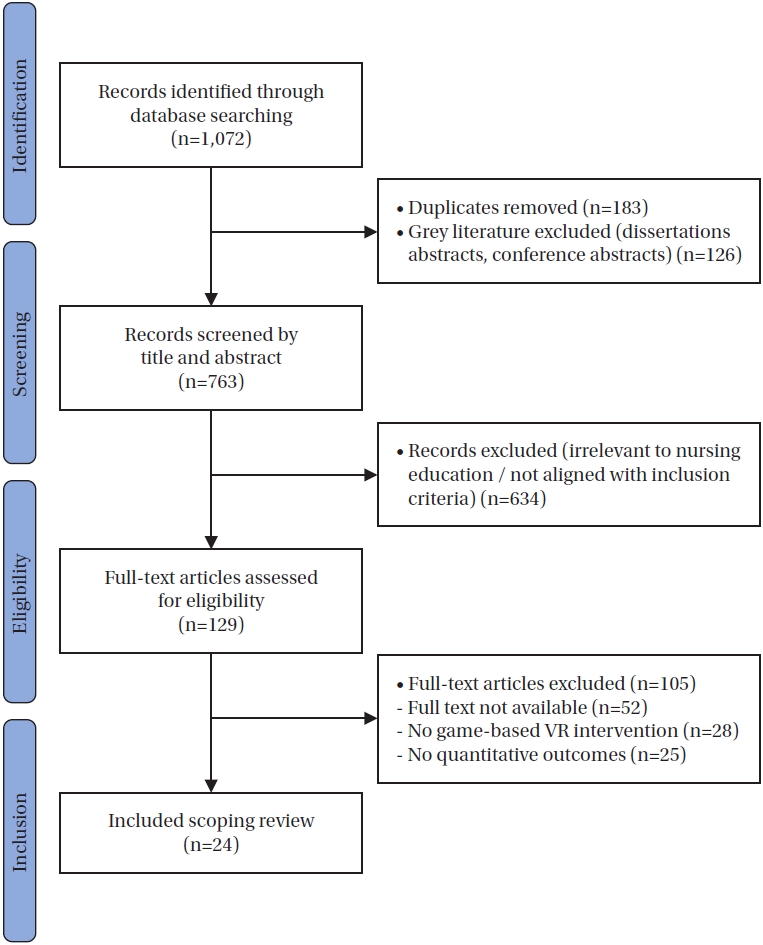
Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

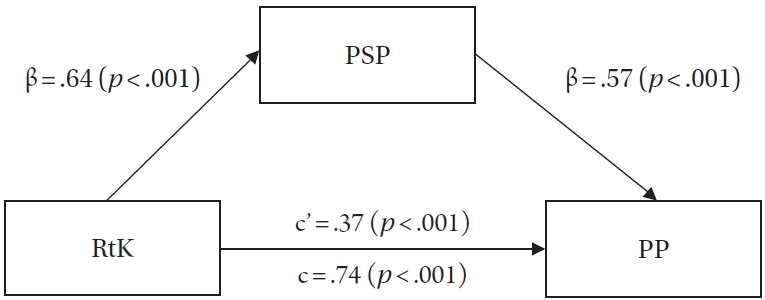
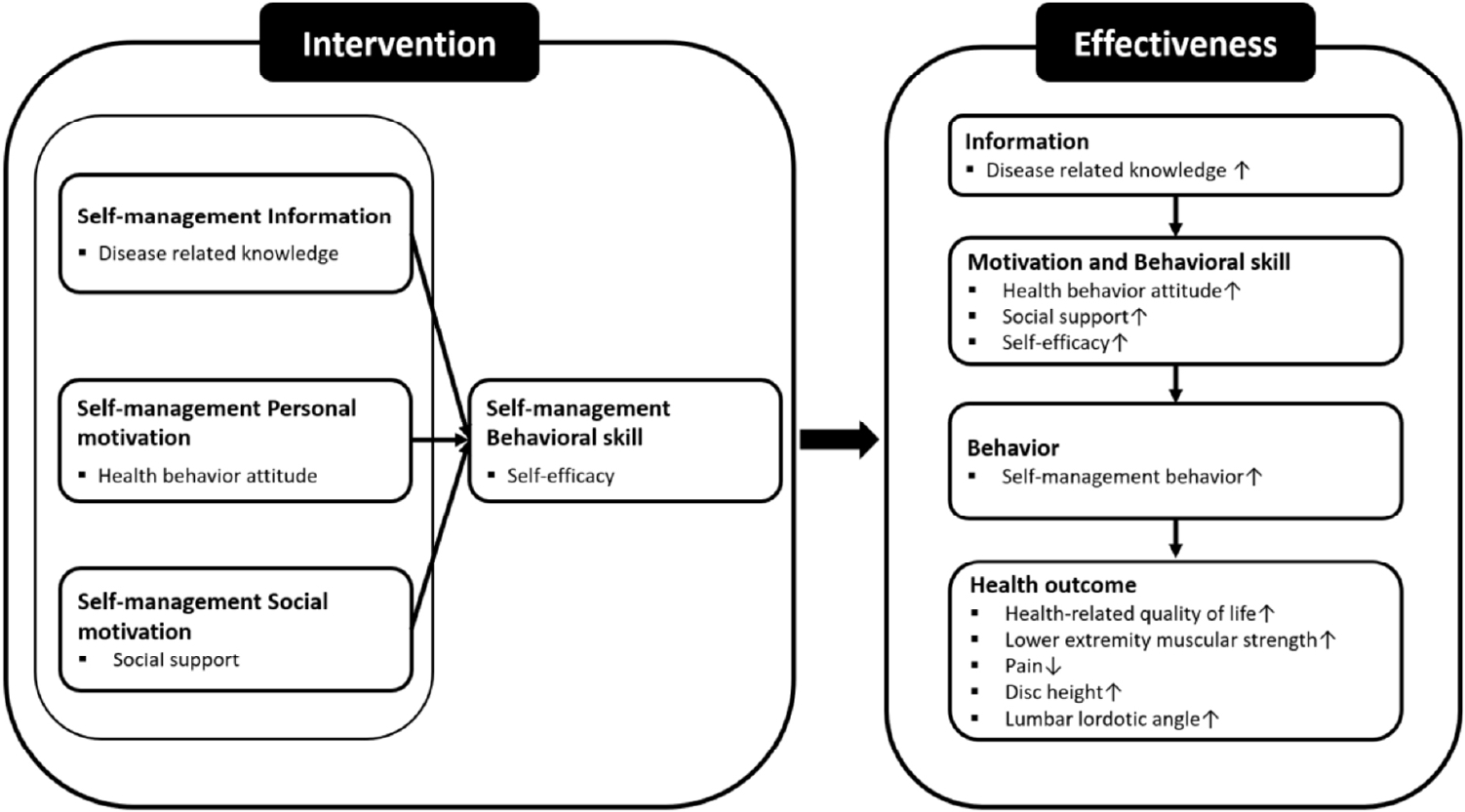
Citations

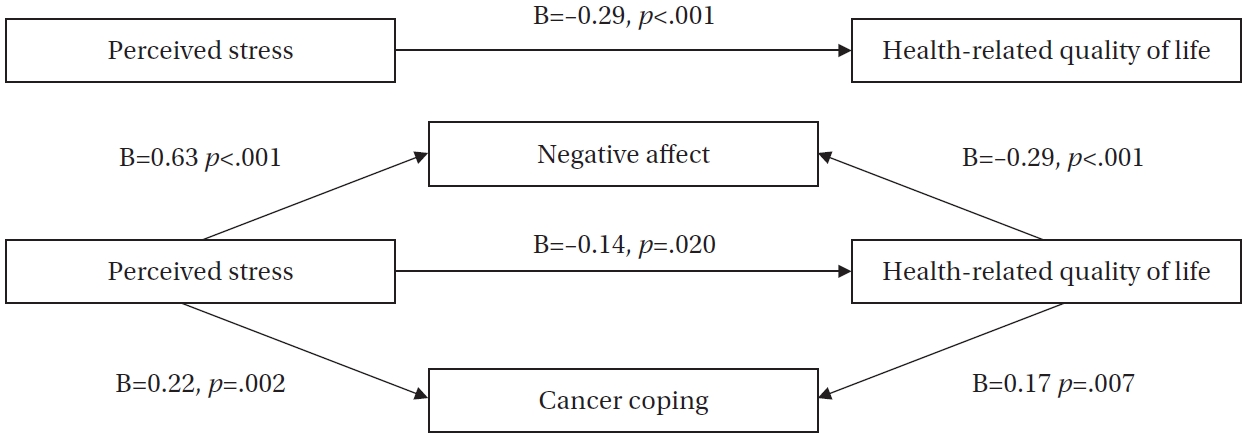
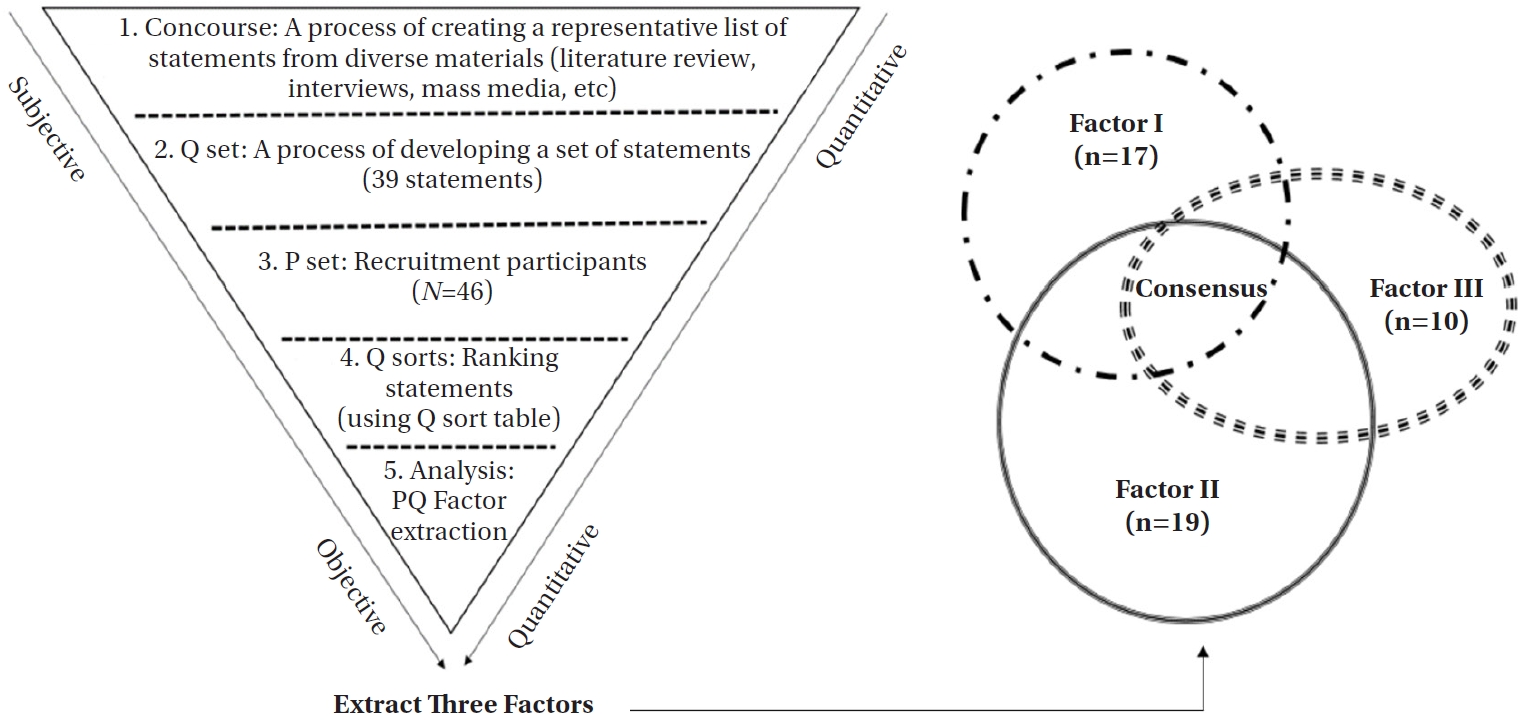
Citations


