1College of Nursing, Graduate School, Pusan National University, Yangsan
2College of Nursing, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea
Copyright © 2015 Korean Society of Adult Nursing
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
| Characteristics | Categories | Total (n=85) | Exp. I (n=30) | Exp. II (n=25) | Com. (n=30) | x2 or F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | ||||
| Age (year) | 68.9±4.1 | 68.6±4.1 | 68.5±4.2 | 69.4±4.3 | 0.08 | .963 | |
| <70 | 47 (55.3) | 17 (56.7) | 14 (56.0) | 16 (53.3) | |||
| ≥70 | 38 (44.7) | 13 (43.3) | 11 (44.0) | 14 (46.7) | |||
| (range) | (60~78) | (60~75) | (60~75) | (61~78) | |||
| Spouse† | Yes | 83 (97.6) | 29 (96.7) | 24 (96.0) | 30 (100.0) | 1.41 | .748 |
| No | 2 (2.4) | 1 (3.3) | 1 (4.0) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| Education† | Elementary school | 13 (15.3) | 4 (13.3) | 4 (16.0) | 5 (16.7) | 2.71 | .867 |
| Middle school | 32 (37.6) | 11 (36.7) | 10 (40.0) | 11 (36.7) | |||
| High school | 30 (35.3) | 11 (36.7) | 10 (40.0) | 9 (30.0) | |||
| ≥College | 10 (11.8) | 4 (13.3) | 1 (4.0) | 5 (16.7) | |||
| Income (10,000 won)† | <100 | 37 (43.5) | 12 (40.0) | 11 (44.0) | 14 (46.7) | 1.90 | .979 |
| ≥100~<200 | 30 (35.3) | 11 (36.7) | 8 (32.0) | 11 (36.7) | |||
| ≥200~<300 | 16 (18.8) | 6 (20.0) | 5 (20.0) | 5 (16.7) | |||
| ≥300 | 2 (2.4) | 1 (3.3) | 1 (4.0) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| Subjective health status | 6.08±1.73 | 6.33±1.45 | 6.20±1.58 | 5.73±2.08 | 0.98 | .380 | |
| Surgery type† | Open | 25 (29.4) | 6 (20.0) | 11 (44.0) | 8 (26.7) | 30.67 | <.001 |
| Laparoscopic | 46 (54.1) | 10 (33.3) | 14 (56.0) | 22 (73.3) | |||
| Robotic | 14 (16.5) | 14 (46.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| Perceived severity of UI† | Mild | 75 (88.2) | 27 (90.0) | 22 (88.0) | 26 (86.7) | 0.84 | 1.000 |
| Moderate | 7 (8.2) | 2 (6.7) | 2 (8.0) | 3 (10.0) | |||
| Severe | 3 (3.5) | 1 (3.3) | 1 (4.0) | 1 (3.3) | |||
| UF related satisfaction | 43.29±5.94 | 43.57±5.89 | 43.16±6.99 | 43.13±5.18 | 0.05 | .953 | |
| Depression† | <5 (Normal) | 2.84±2.26 | 2.77±2.34 | 2.88±2.42 | 2.87±2.11 | 0.02 | .979 |
| 6~9 (Mild DP) | 74 (87.1) | 26 (86.7) | 21 (84.0) | 27 (90.0) | 2.24 | .795 | |
| ≥10 (Severe DP) | 9 (10.6) | 3 (10.0) | 4 (16.0) | 2 (6.7) | |||
| 2 (2.4) | 1 (3.3) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.3) | ||||
| Quality of life | 111.14±15.01 | 111.37±11.32 | 115.40±14.60 | 107.37±17.82 | 2.01 | .141 | |
| (range) | (67~136) | (79~128) | (79~135) | (67~136) | |||
| Characteristics | Categories | Exp. I (n=30)a | Exp. II (n=25)b | Com. (n=30)c | Differences between groups | Differences according to the ST | Differences as time passage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | x2 or F (p) | Tukey HSD (p) | F (p) | F (p) | ||||
| Performance of PFME | 1M | 16.37±2.59 | 15.20±4.04 | 13.87±3.30 | 4.26 (.017) | a>c (.001) | 1.72 (.186) | |||
| 3M | 16.23±2.74 | 14.91±2.64 | 13.27±3.70 | 6.89 (.002) | a>c (.015) | 1.27 (.287) | ||||
| Perceived severity of UI† | 1M | Mild Moderate Severe | 24 (80.0) | 19 (76.0) | 10 (33.3) | 15.96 (.002) | ||||
| 4 (13.3) | 4 (16.0) | 12 (40.0) | ||||||||
| 2 (6.7) | 2 (8.0) | 8 (26.7) | ||||||||
| 3M | Mild Moderate Severe | 28 (93.3) | 21 (91.3) | 20 (66.7) | 11.62 (.006) | |||||
| 0 (0.0) | 1 (4.3) | 8 (26.7) | ||||||||
| 2 (6.7) | 1 (4.3) | 2 (6.7) | ||||||||
| UF related satisfaction | Pre | 43.57±5.89 | 43.16±6.99 | 43.13±5.18 | 0.05 (.953) | 0.99 (.378) | Group | 2.09 (.130) | ||
| 1M | 37.87±6.17 | 36.64±6.66 | 32.93±7.17 | 4.39 (.015) | a>c (.015) | 0.12 (.888) | Time | 62.44 (<.001) | ||
| 3M | 42.50±6.35 | 39.43±8.17 | 39.00±6.38 | 2.23 (.114) | 0.42 (.661) | G*T | 3.09 (.017) | |||
| Depression | Pre | 2.77±2.34 | 2.88±2.42 | 2.87±2.11 | 0.02 (.979) | 1.64 (.201) | Group | 1.03 (.360) | ||
| 1M | 3.70±3.47 | 4.28±3.52 | 5.53±3.59 | 2.11 (.128) | 0.12 (.885) | Time | 40.72 (<.001) | |||
| 3M | 1.60±2.06 | 2.35±3.26 | 2.43±2.75 | 0.85 (.431) | 0.29 (.753) | G*T | 1.95 (.107) | |||
| Quality of life | Pre | 111.37±11.32 | 115.40±14.60 | 107.37±17.82 | 2 2.01 (.141) | 2.29 (.108) | Group | 3.96 (.023) | ||
| 1M | 96.17±20.04 | 92.12±25.98 | 85.37±20.67 | 7 1.82 (.169) | 0.96 (.387) | Time | 91.53 (<.001) | |||
| 3M | 113.77±17.68 | 117.04±21.53 | 98.60±15.57 | 7 8.24 (.001) | a>c (.005), | 0.79 (.459) | G*T | 3.66 (.007) | ||
| b>c (.001) | ||||||||||

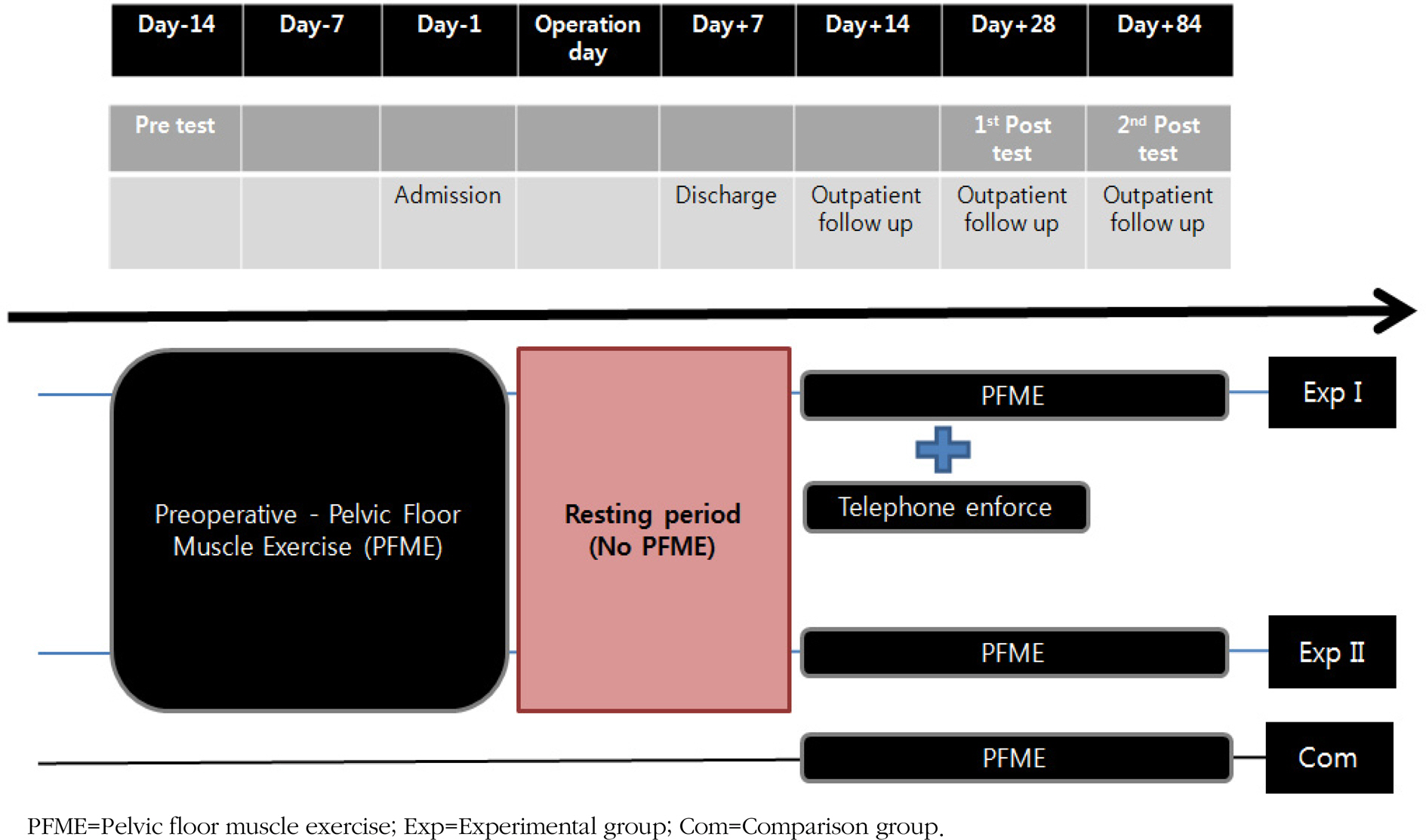
Characteristics of the Participants (N=85)
| Characteristics | Categories | Total (n=85) | Exp. I (n=30) | Exp. II (n=25) | Com. (n=30) | x2 or F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | ||||
| Age (year) | 68.9±4.1 | 68.6±4.1 | 68.5±4.2 | 69.4±4.3 | 0.08 | .963 | |
| <70 | 47 (55.3) | 17 (56.7) | 14 (56.0) | 16 (53.3) | |||
| ≥70 | 38 (44.7) | 13 (43.3) | 11 (44.0) | 14 (46.7) | |||
| (range) | (60~78) | (60~75) | (60~75) | (61~78) | |||
| Spouse |
Yes | 83 (97.6) | 29 (96.7) | 24 (96.0) | 30 (100.0) | 1.41 | .748 |
| No | 2 (2.4) | 1 (3.3) | 1 (4.0) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| Education |
Elementary school | 13 (15.3) | 4 (13.3) | 4 (16.0) | 5 (16.7) | 2.71 | .867 |
| Middle school | 32 (37.6) | 11 (36.7) | 10 (40.0) | 11 (36.7) | |||
| High school | 30 (35.3) | 11 (36.7) | 10 (40.0) | 9 (30.0) | |||
| ≥College | 10 (11.8) | 4 (13.3) | 1 (4.0) | 5 (16.7) | |||
| Income (10,000 won) |
<100 | 37 (43.5) | 12 (40.0) | 11 (44.0) | 14 (46.7) | 1.90 | .979 |
| ≥100~<200 | 30 (35.3) | 11 (36.7) | 8 (32.0) | 11 (36.7) | |||
| ≥200~<300 | 16 (18.8) | 6 (20.0) | 5 (20.0) | 5 (16.7) | |||
| ≥300 | 2 (2.4) | 1 (3.3) | 1 (4.0) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| Subjective health status | 6.08±1.73 | 6.33±1.45 | 6.20±1.58 | 5.73±2.08 | 0.98 | .380 | |
| Surgery type |
Open | 25 (29.4) | 6 (20.0) | 11 (44.0) | 8 (26.7) | 30.67 | <.001 |
| Laparoscopic | 46 (54.1) | 10 (33.3) | 14 (56.0) | 22 (73.3) | |||
| Robotic | 14 (16.5) | 14 (46.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| Perceived severity of UI |
Mild | 75 (88.2) | 27 (90.0) | 22 (88.0) | 26 (86.7) | 0.84 | 1.000 |
| Moderate | 7 (8.2) | 2 (6.7) | 2 (8.0) | 3 (10.0) | |||
| Severe | 3 (3.5) | 1 (3.3) | 1 (4.0) | 1 (3.3) | |||
| UF related satisfaction | 43.29±5.94 | 43.57±5.89 | 43.16±6.99 | 43.13±5.18 | 0.05 | .953 | |
| Depression |
<5 (Normal) | 2.84±2.26 | 2.77±2.34 | 2.88±2.42 | 2.87±2.11 | 0.02 | .979 |
| 6~9 (Mild DP) | 74 (87.1) | 26 (86.7) | 21 (84.0) | 27 (90.0) | 2.24 | .795 | |
| ≥10 (Severe DP) | 9 (10.6) | 3 (10.0) | 4 (16.0) | 2 (6.7) | |||
| 2 (2.4) | 1 (3.3) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.3) | ||||
| Quality of life | 111.14±15.01 | 111.37±11.32 | 115.40±14.60 | 107.37±17.82 | 2.01 | .141 | |
| (range) | (67~136) | (79~128) | (79~135) | (67~136) | |||
Exp.=experimental group; Com.=comparison group; UI=urinary incontinence; UF=urinary function; DP=depressives;
†Fisher's exact test.
Effects of Pre-Operative Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercise (PFME) and Telephone Enforcement on the Performance of PFME, Perceived Severity of Urinary Incontinence, Urinary Function related Satisfaction, Depression, and Quality of Life (N=85)
| Characteristics | Categories | Exp. I (n=30)a | Exp. II (n=25)b | Com. (n=30)c | Differences between groups | Differences according to the ST | Differences as time passage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | x2 or F (p) | Tukey HSD (p) | F (p) | F (p) | ||||
| Performance of PFME | 1M | 16.37±2.59 | 15.20±4.04 | 13.87±3.30 | 4.26 (.017) | a>c (.001) | 1.72 (.186) | |||
| 3M | 16.23±2.74 | 14.91±2.64 | 13.27±3.70 | 6.89 (.002) | a>c (.015) | 1.27 (.287) | ||||
| Perceived severity of UI |
1M | Mild Moderate Severe | 24 (80.0) | 19 (76.0) | 10 (33.3) | 15.96 (.002) | ||||
| 4 (13.3) | 4 (16.0) | 12 (40.0) | ||||||||
| 2 (6.7) | 2 (8.0) | 8 (26.7) | ||||||||
| 3M | Mild Moderate Severe | 28 (93.3) | 21 (91.3) | 20 (66.7) | 11.62 (.006) | |||||
| 0 (0.0) | 1 (4.3) | 8 (26.7) | ||||||||
| 2 (6.7) | 1 (4.3) | 2 (6.7) | ||||||||
| UF related satisfaction | Pre | 43.57±5.89 | 43.16±6.99 | 43.13±5.18 | 0.05 (.953) | 0.99 (.378) | Group | 2.09 (.130) | ||
| 1M | 37.87±6.17 | 36.64±6.66 | 32.93±7.17 | 4.39 (.015) | a>c (.015) | 0.12 (.888) | Time | 62.44 (<.001) | ||
| 3M | 42.50±6.35 | 39.43±8.17 | 39.00±6.38 | 2.23 (.114) | 0.42 (.661) | G*T | 3.09 (.017) | |||
| Depression | Pre | 2.77±2.34 | 2.88±2.42 | 2.87±2.11 | 0.02 (.979) | 1.64 (.201) | Group | 1.03 (.360) | ||
| 1M | 3.70±3.47 | 4.28±3.52 | 5.53±3.59 | 2.11 (.128) | 0.12 (.885) | Time | 40.72 (<.001) | |||
| 3M | 1.60±2.06 | 2.35±3.26 | 2.43±2.75 | 0.85 (.431) | 0.29 (.753) | G*T | 1.95 (.107) | |||
| Quality of life | Pre | 111.37±11.32 | 115.40±14.60 | 107.37±17.82 | 2 2.01 (.141) | 2.29 (.108) | Group | 3.96 (.023) | ||
| 1M | 96.17±20.04 | 92.12±25.98 | 85.37±20.67 | 7 1.82 (.169) | 0.96 (.387) | Time | 91.53 (<.001) | |||
| 3M | 113.77±17.68 | 117.04±21.53 | 98.60±15.57 | 7 8.24 (.001) | a>c (.005), | 0.79 (.459) | G*T | 3.66 (.007) | ||
| b>c (.001) | ||||||||||
Exp.=experimental group; Com.=comparison group; ST=surgery types; PFME=pelvic floor muscle exercise; Pre=pre operation; 1M=Post operation 1 month; 3M=post operation 3 month; UI=urinary incontinence; UF=urinary function; G*S=group*surgery; G*T=group*time;
†Fisher's exact test.
Exp.=experimental group; Com.=comparison group; UI=urinary incontinence; UF=urinary function; DP=depressives; Fisher's exact test.
Exp.=experimental group; Com.=comparison group; ST=surgery types; PFME=pelvic floor muscle exercise; Pre=pre operation; 1M=Post operation 1 month; 3M=post operation 3 month; UI=urinary incontinence; UF=urinary function; G*S=group*surgery; G*T=group*time; Fisher's exact test.