1College of Nursing, Research Institute of Nursing Science, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju
2Division of Nursing, Research Institute of Nursing Science, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea
Copyright © 2015 Korean Society of Adult Nursing
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Rubric for Evaluating the Clinical Reasoning Skill
| Categories | Score and description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Collecting data | 3 Appropriately collects the subjective and objective data related to the patient' s condition | 2 Collects the most obvious data, missing some important information | 1 Confuses the patient's condition and disorganizes the data |
| Diagnosing | 2 Analyzes and synthesizes the data; describes the diagnosis relevant to data | 1 Analyzes and synthesizes the data; describes the diagnosis but less relevant to data | 0 Has difficulty analyzing and synthesizing the data; describes the diagnosis but not relevant to data |
| Prioritizing problem | 2 Focuses on the most relevant and important data to patient's condition | 1 Focuses on data relevant to patient's condition but less important or not priority | 0 Has difficulty with prioritizing; data not relevant to patient's condition |
| Planning | 3 Selects nursing interventions to resolve the problem; appropriately planned interventions based on relevant patient data | 2 Selects nursing interventions to resolve the problem; less appropriately planned interventions based on most obvious data | 1 Selects a single intervention, addressing a likely solution, but it may be vague, confusing, and/or incomplete |
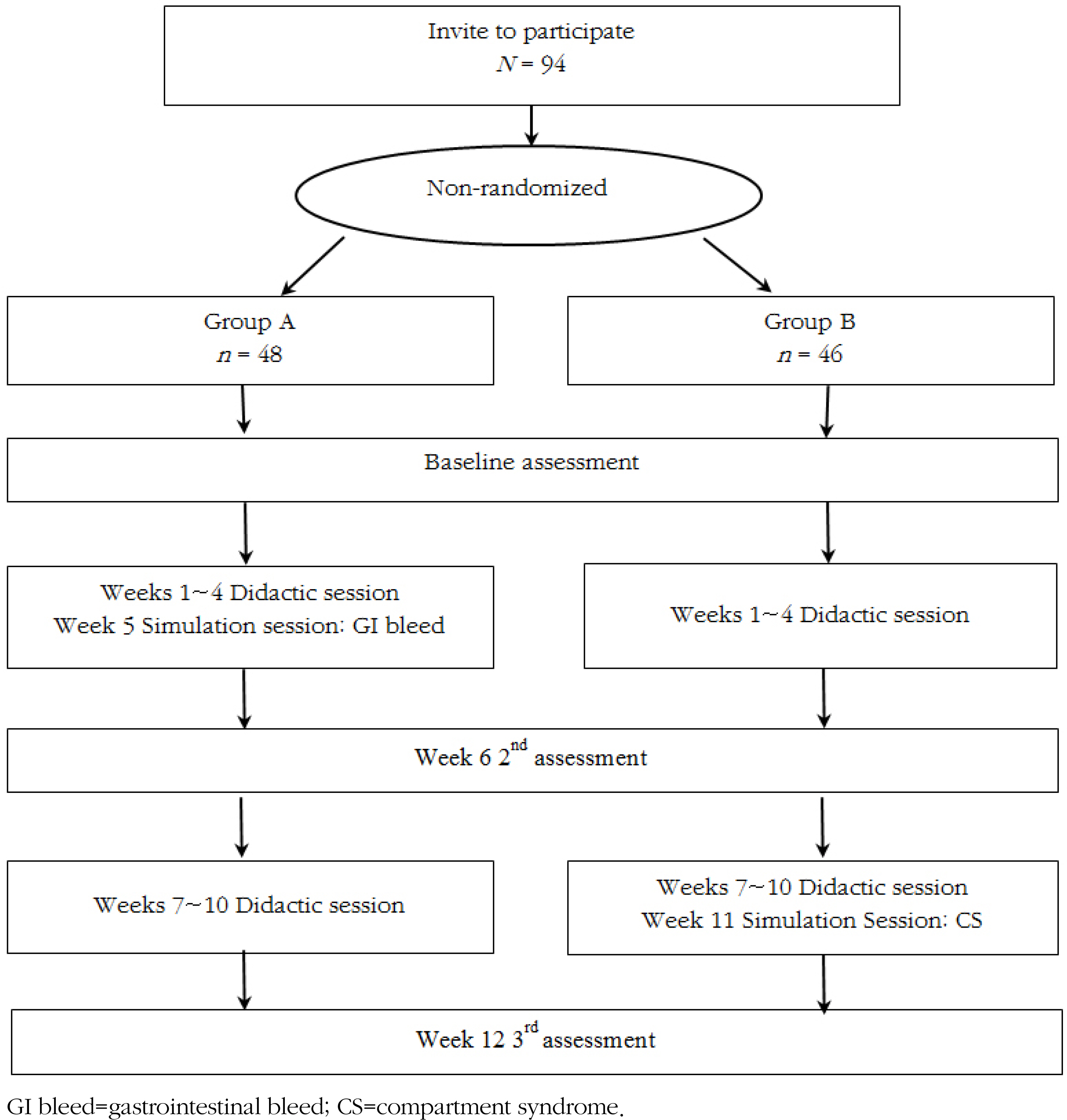
Homogeneity of the Participants' Characteristics between the Groups (N=94)
| Characteristics | Categories | Group A (n=48) | Group B (n=46) | x2 or t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | ||||
| Gender | Male | 6 (12.5) | 5 (10.9) | 0.06 | .806 |
| Female | 42 (87.5) | 41 (89.1) | |||
| Age (year) | 21.06±1.80 | 20.98±1.35 | 0.26 | .799 | |
| Satisfaction for nursing major | 3.60±0.71 | 3.50±0.86 | 0.64 | .523 | |
| Grade point average (GPA) | 3.59±0.46 | 3.53±0.43 | 0.64 | .523 | |
| Self-confidence for GI bleed | 33.09±5.44 | 32.60±5.75 | 0.46 | .679 | |
| Self-confidence for CS | 33.90±5.60 | 33.33±7.54 | 0.41 | .682 |
GI bleed=gastrointestinal bleed; CS=compartment syndrome.
Comparison of Knowledge, Clinical Reasoning, and Self-confidence between the Groups (N=94)
| Variables | Categories | Group (n) | M±SD | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge for GI bleed | Simulation/lecture | A (48) | 6.83±1.93 | 2.55 | .012 |
| Lecture only | B (46) | 5.70±2.38 | |||
| Clinical reasoning for GI bleed | Simulation/lecture | A (48) | 6.34±1.88 | 2.83 | .006 |
| Lecture only | B (46) | 5.22±1.94 | |||
| Self-confidence for GI bleed | Simulation/lecture | A (48) | 37.56±6.03 | -0.81 | .418 |
| Lecture only | B (46) | 38.50±5.09 | |||
| Knowledge for CS | Simulation/lecture | B (46) | 7.30±1.99 | -2.11 | .038 |
| Lecture only | A (48) | 6.29±2.64 | |||
| Clinical reasoning for CS | Simulation/lecture | B (46) | 7.57±1.67 | -3.60 | .001 |
| Lecture only | A (48) | 6.29±1.76 | |||
| Self-confidence for CS | Simulation/lecture | B (46) | 38.13±6.55 | 1.10 | .276 |
| Lecture only | A (48) | 39.53±5.76 |
GI bleed=gastrointestinal bleed; CS=compartment syndrome.
GI bleed=gastrointestinal bleed; CS=compartment syndrome.
GI bleed=gastrointestinal bleed; CS=compartment syndrome.