1Nurse, Gangnam Severance Hospital ․ Doctoral Student, Hanyang University, Seoul
2Professor, College of Nursing, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea
Copyright © 2016 Korean Society of Adult Nursing
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
| Variables | Categories | n(%) | M±SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk factors for CVD† | Hypertension | 99 (72.8) | |
| Diabetes | 26 (19.1) | ||
| Dyslipidemia | 46 (33.8) | ||
| Angina | 33 (24.2) | ||
| Arrhythmia, fat liver, arthritis | 25 (18.3) | ||
| CVD risk classification |
High risk‡ group At risk§ group |
52 (38.2) 84 (61.8) |
|
| Family history† | Yes | 65 (47.8) | |
| Hypertension | 40 (29.4) | ||
| Angina, CAOD, Stroke | 38 (28.0) | ||
| Diabetes | 22 (16.2) | ||
| Etc | 2 (1.5) | ||
| Waist-hip ratio (n=131) | >0.85 | 106 (80.9) | 0.93±0.75 |
| ≤0.85 | 25 (19.1) | ||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | ≤25 | 41 (30.1) | 24.93±4.03 |
| >25~29 | 37 (27.2) | ||
| ≥30 | 58 (42.7) | ||
| Waist-height ratio (n=131) | >0.52 | 53 (40.5) | 0.54±0.08 |
| ≤0.51 | 78 (59.5) |
CVD=cardiocerebrovascular disease; CAOD=coronary artery occlusive disease;
†Multiple response;
‡High risk includes the presence of documented CVD, diabetes, end-stage renal disease, 10-year predicted risk for CVD ≥10%;
§At risk includes the presence of ≥1 major risk factors, metabolic syndrome, evidence of subclinical vascular disease, treated hypertension.

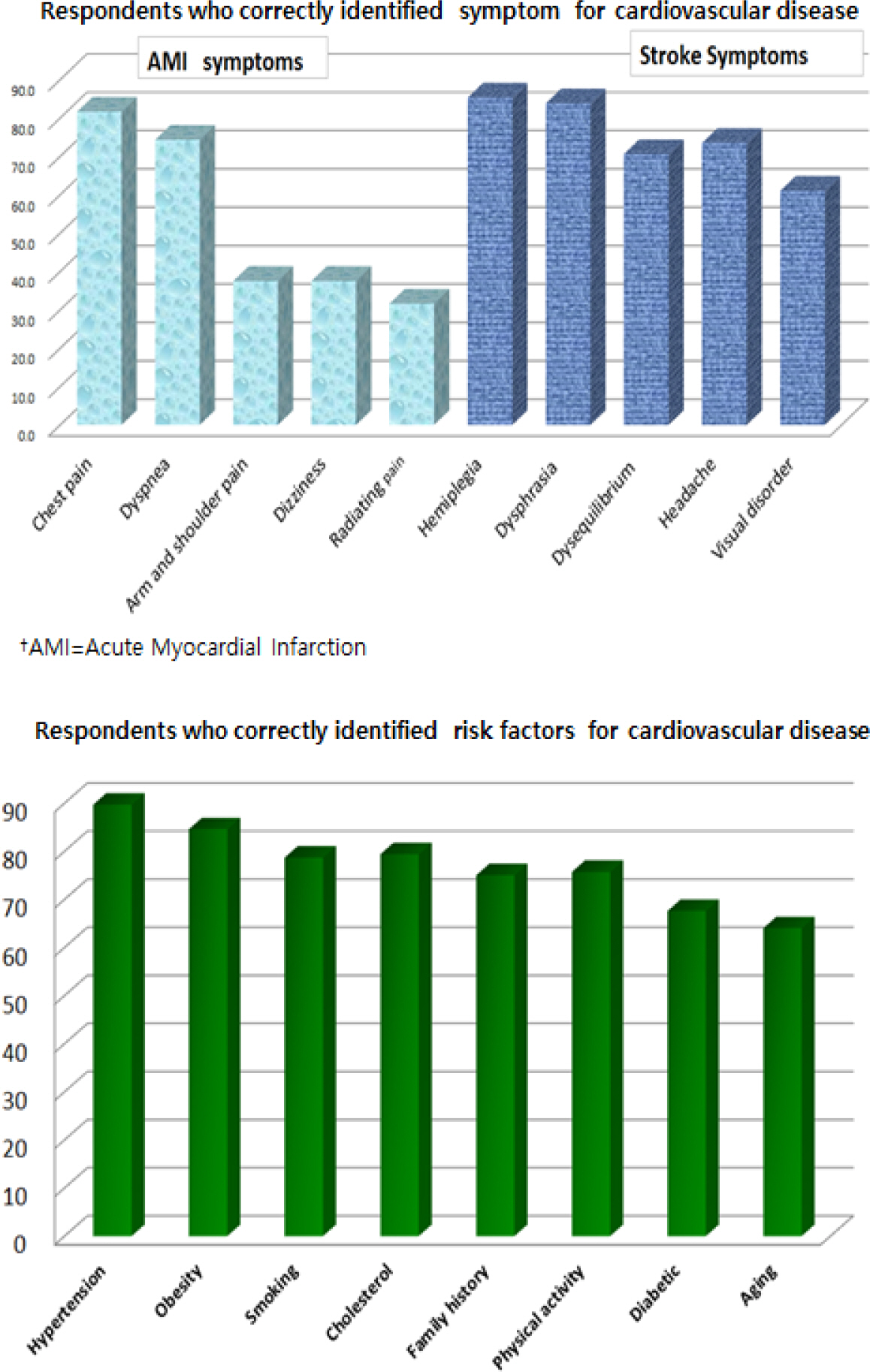
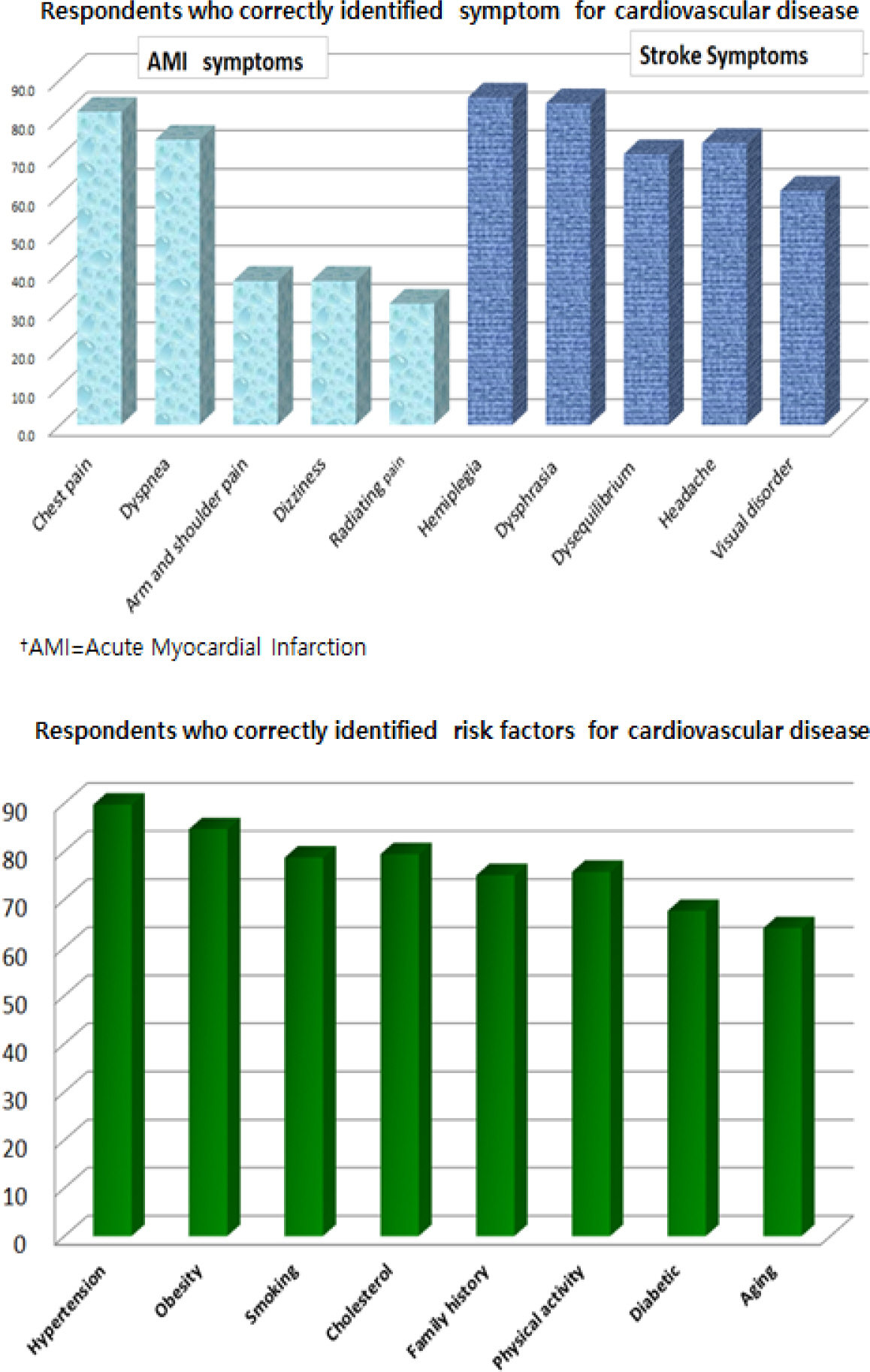
Sociodemographic Characteristics of the Participants (N=136)
| Characteristics | Categories | n(%) | M±SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 45~59 | 52 (38.2) | 60.7±6.5 |
| 60~69 | 84 (61.8) | ||
| Education level | ≥High school | 74 (54.4) | |
| ≤Middle school | 58 (42.6) | ||
| Marital status | Married | 104 (76.5) | |
| Widowed, single, divorced | 32 (23.5) | ||
| Living with | Spouse or children | 105 (82.0) | |
| Alone | 23 (18.0) | ||
| Household monthly income (10,000 won) | <100 | 32 (24.1) | |
| 100~300 | 53 (39.8) | ||
| ≥300 | 48 (36.1) | ||
| Job | Yes | 43 (32.1) | |
| None or housewife | 91 (67.9) | ||
| Regular physical exercise | ≥3/week | 48 (26.1) | |
| <3/week | 51 (38.1) | ||
| None | 48 (35.8) | ||
| Age at menopause | 50.52±4.11 | ||
| Experience of physical examination | Yes | 89 (65.9) | |
| No | 46 (34.1) | ||
| Education experience for CVD prevention | Yes | 36 (26.5) | |
| No | 100 (73.5) | ||
| Information source on CVD | Television | 81 (64.8) | |
| Hospital | 37 (29.6) | ||
| Public health center & newspaper | 7 (5.6) | ||
| Perceived risk of CVD incidence | Occasionally & frequently | 101 (74.3) | |
| None | 35 (25.7) | ||
| Awareness of AMI and stroke in the usual | I know well & try to be careful | 100 (73.5) | |
| Not mind | 36 (26.5) | ||
| Expected action when witnessed stroke or heart attack | Call 119 | 117 (86.1) | |
| I don't know | 19 (13.9) | ||
| Awareness of CVD risk increase after menopause | I know | 56 (41.5) | |
| I don't know | 79 (58.5) | ||
| Hormone therapy experience | Yes | 29 (24.5) | |
| No | 89 (75.5) |
Disease-related Characteristics of the Participants (N=136)
| Variables | Categories | n(%) | M±SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk factors for CVD |
Hypertension | 99 (72.8) | |
| Diabetes | 26 (19.1) | ||
| Dyslipidemia | 46 (33.8) | ||
| Angina | 33 (24.2) | ||
| Arrhythmia, fat liver, arthritis | 25 (18.3) | ||
| CVD risk classification | High risk At risk |
52 (38.2) 84 (61.8) |
|
| Family history |
Yes | 65 (47.8) | |
| Hypertension | 40 (29.4) | ||
| Angina, CAOD, Stroke | 38 (28.0) | ||
| Diabetes | 22 (16.2) | ||
| Etc | 2 (1.5) | ||
| Waist-hip ratio (n=131) | >0.85 | 106 (80.9) | 0.93±0.75 |
| ≤0.85 | 25 (19.1) | ||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | ≤25 | 41 (30.1) | 24.93±4.03 |
| >25~29 | 37 (27.2) | ||
| ≥30 | 58 (42.7) | ||
| Waist-height ratio (n=131) | >0.52 | 53 (40.5) | 0.54±0.08 |
| ≤0.51 | 78 (59.5) |
CVD=cardiocerebrovascular disease; CAOD=coronary artery occlusive disease;
†Multiple response;
‡High risk includes the presence of documented CVD, diabetes, end-stage renal disease, 10-year predicted risk for CVD ≥10%;
§At risk includes the presence of ≥1 major risk factors, metabolic syndrome, evidence of subclinical vascular disease, treated hypertension.
Knowledge and Health Behavior for CVD Prevention (N=136)
| Variables | Categories | n (%) or M±SD |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge for CVD prevention | Nicotine in cigarettes makes it increased your blood pressure, pulse | 98 (72.1) |
| Even if you smoke yourself, secondhand smoke is harmful to health | 133 (97.8) | |
| Moderate exercise is good treatment for smoking cessation | 103 (75.7) | |
| After drinking alcohol shed a lot of sweat in the sauna Alcoholic minutes to exit the sweat liquor wakes up soon | 110 (80.9) | |
| Regardless of the amount of drinking, do not drink at least three days in order to protect the liver | 91 (66.9) | |
| Egg yolk, quail egg, and shrimp should be restricted because it contains a lot of cholesterol | 104 (76.5) | |
| When consumed for a long time, salty foods can be elevated blood pressure | 125 (91.9) | |
| Excessive intake of high-carbohydrate (rice, bread, chocolate, coffee, etc.), it would increase the triglycerides | 99 (72.8) | |
| Fiber foods is good to prevent the accumulation of cholesterol and obesity | 113 (83.1) | |
| Weight control is helpful in hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia prevention | 125 (91.9) | |
| Exercises reduces LDL increases the HDL | 115 (84.6) | |
| It is effective in preventing metabolic syndrome that shorten the high intensity (running, soccer) than to continue the light exercises (walking, cycling slowly) | 71 (52.2) | |
| Rapid and nervous personalities are more vulnerable to stress than relaxed and optimistic personality | 119 (87.5) | |
| Health behavior for CVD prevention | Regularly measure blood pressure | 3.53±1.14 |
| Regularly measure blood glucose | 2.66±1.36 | |
| According to the doctor's prescription and taking medication | 4.16±1.04 | |
| It has received regular checks complications | 3.21±1.33 | |
| Has maintaining a standard body weight | 2.76±1.19 | |
| It maintains a waist circumference within the normal range | 2.69±1.17 | |
| Keeping the amount of food | 3.15±1.16 | |
| Maintain a low salt diet | 3.02±1.23 | |
| Each time you eat a meal of vegetables other than kimchi. | 3.54±1.01 | |
| 30 minutes/once, and exercise more than 3 times a week | 2.85±1.44 | |
| 30 minutes/once, and exercise more than 5 times a week | 2.49±1.37 | |
| Do not drink | 4.35±1.04 | |
| No smoking | 4.69±0.94 | |
| It has good stress management | 3.07±1.16 | |
| Sleep more than seven hours a day enough | 2.94±1.26 | |
| Sum | 49.10±9.64 |
CVD=cardio-cerebrovascular disease; HDL=high-density lipoprotein; LDL=low-density lipoprotein.
Predicting Factors on Health Behavior for CVD Prevention (N=136)
| Variables | B | SE | β | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Constant) | 24.71 | 10.34 | 2.39 | <.001 | |
| Age | 0.14 | 0.13 | .09 | 1.10 | .274 |
| Marital status | 2.10 | 1.06 | .19 | 1.98 | .057 |
| Living with family | 6.27 | 2.27 | .26 | 2.76 | .007 |
| Waist-hip ratio (≤0.85) | 4.49 | 1.97 | .19 | 2.28 | .024 |
| Awareness of AMI and stroke in the usual | 3.25 | 0.86 | .31 | 3.77 | <.001 |
| R2=.21, Adjusted R2=.17, F=6.05, p<.001 | |||||
CVD=cardio-cerebrovascular disease; AMI=acute myocardial infarction.
CVD=cardiocerebrovascular disease; CAOD=coronary artery occlusive disease; Multiple response; High risk includes the presence of documented CVD, diabetes, end-stage renal disease, 10-year predicted risk for CVD ≥10%; At risk includes the presence of ≥1 major risk factors, metabolic syndrome, evidence of subclinical vascular disease, treated hypertension.
CVD=cardio-cerebrovascular disease; HDL=high-density lipoprotein; LDL=low-density lipoprotein.
CVD=cardio-cerebrovascular disease; AMI=acute myocardial infarction.