1Assistant Professor, Department of Nursing, Teagu Science University, Daegu
2Assistant Professor, College of Nursing, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea
Copyright © 2017 Korean Society of Adult Nursing
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
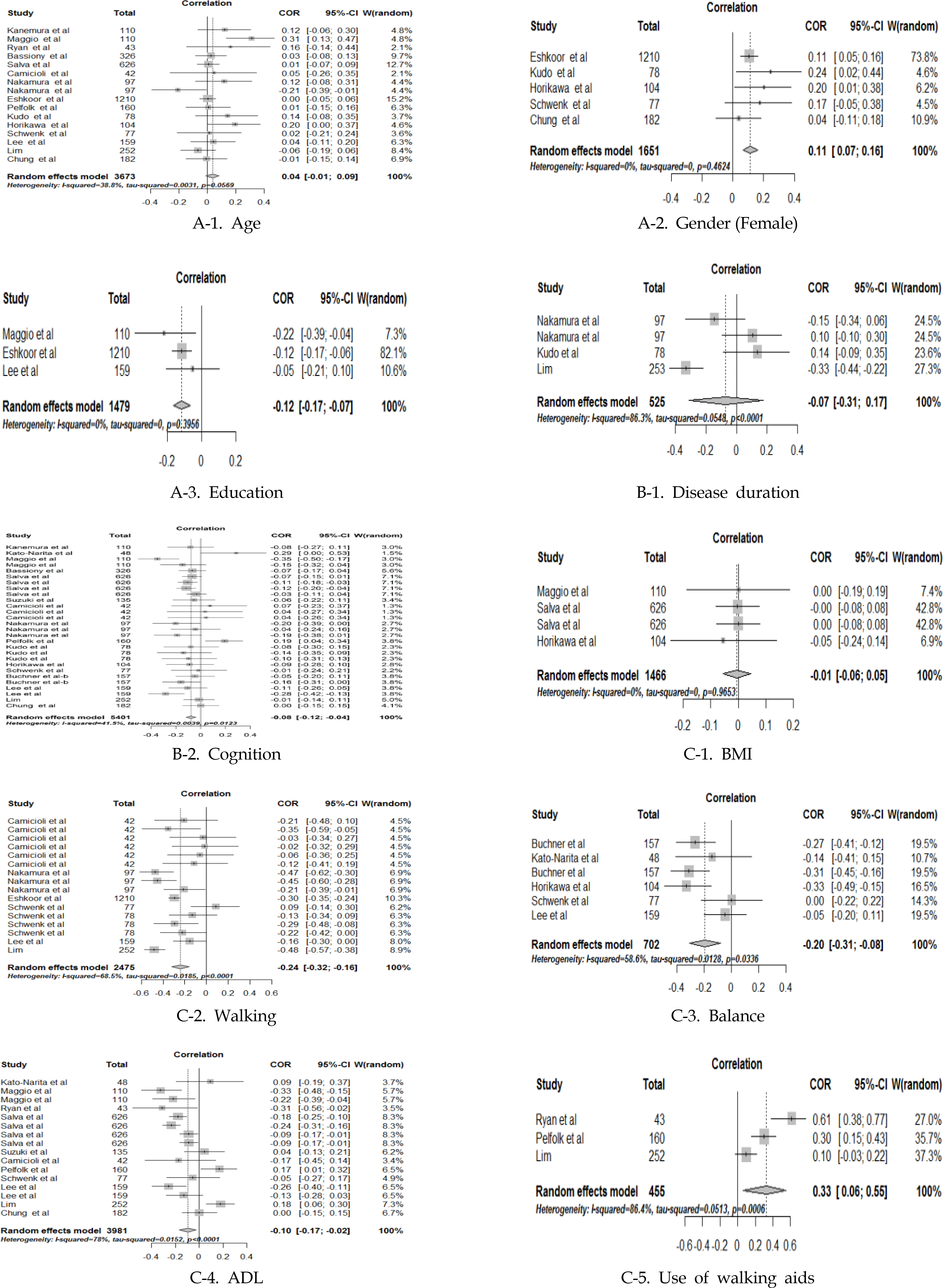
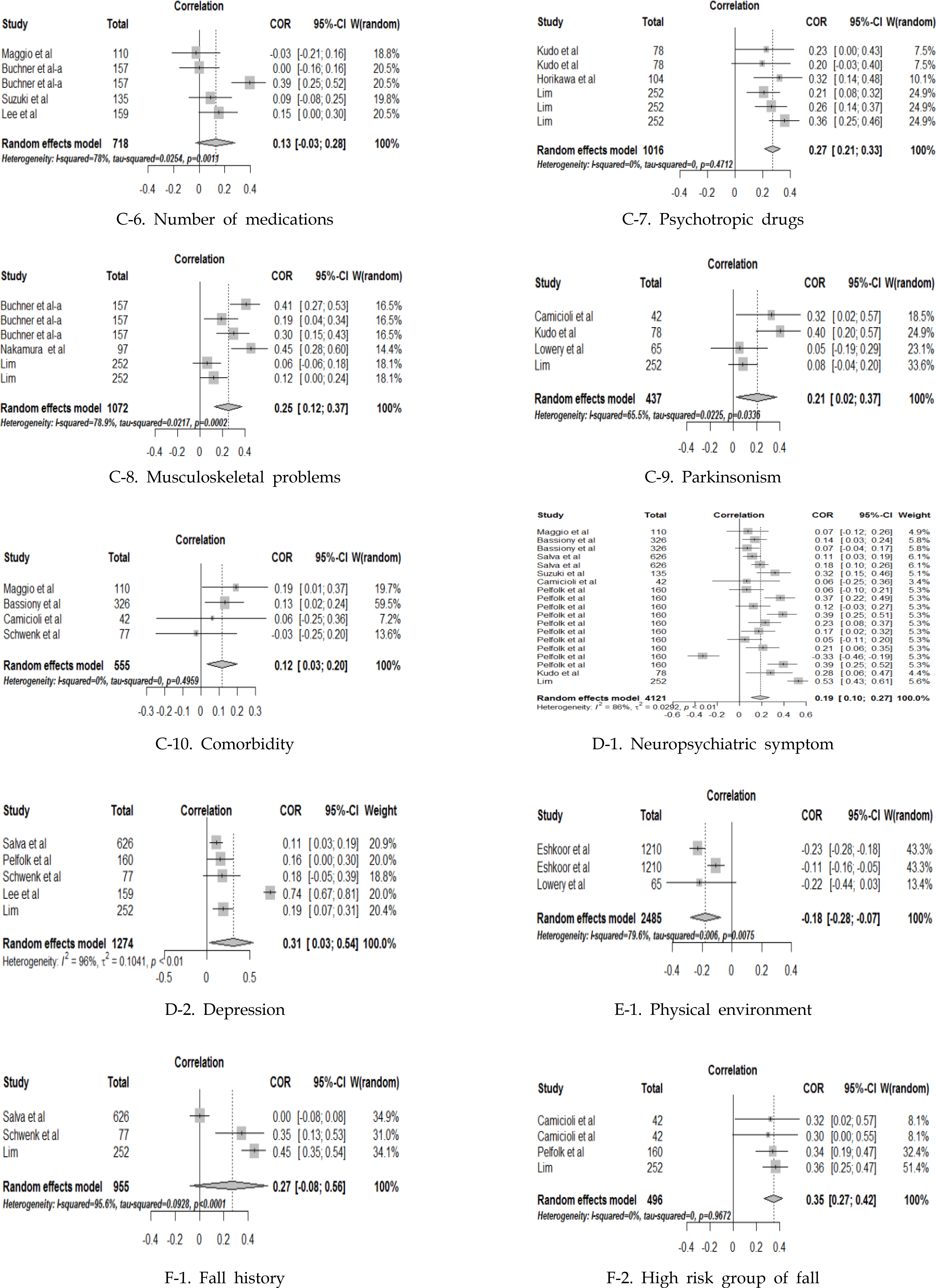

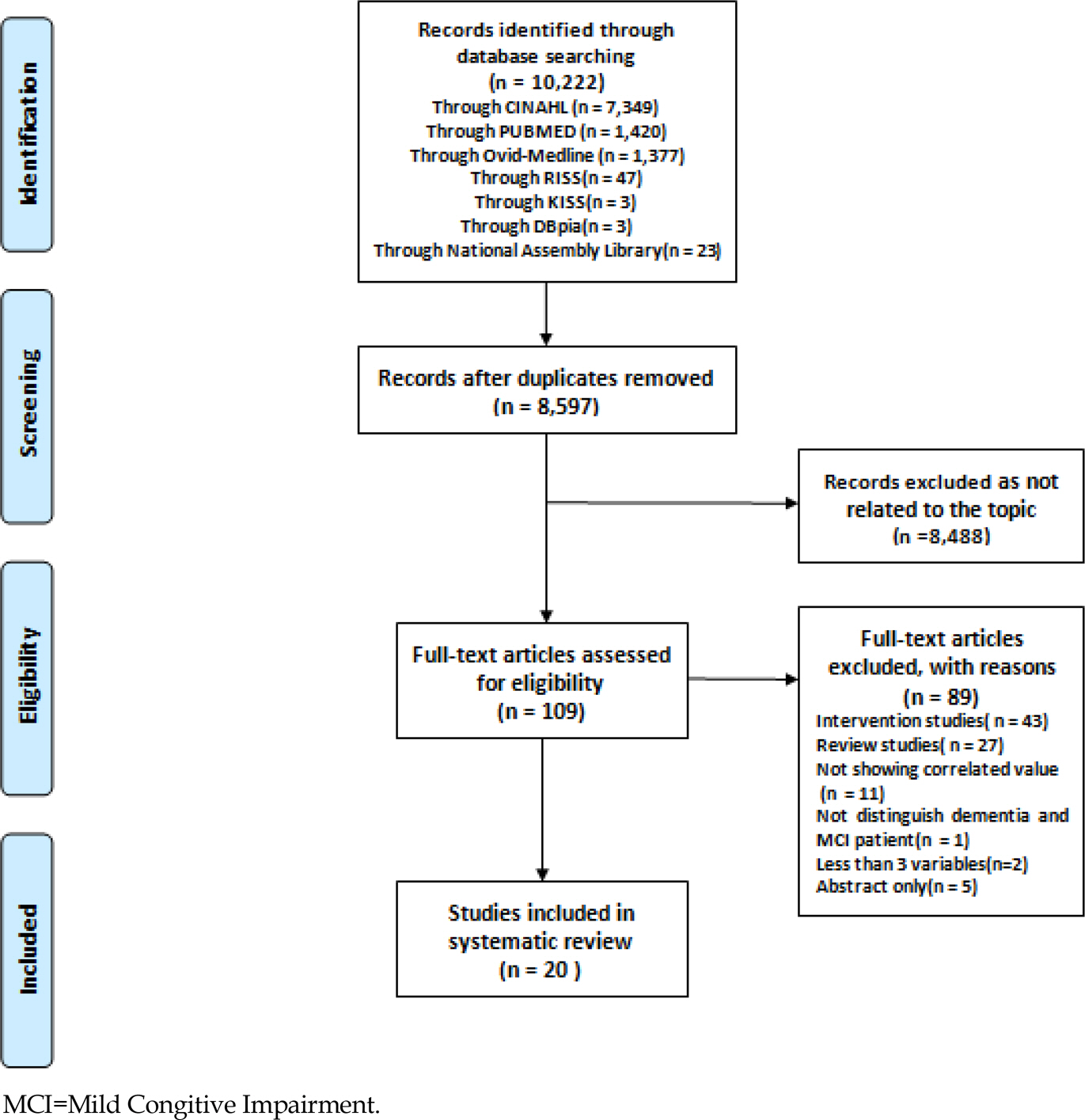
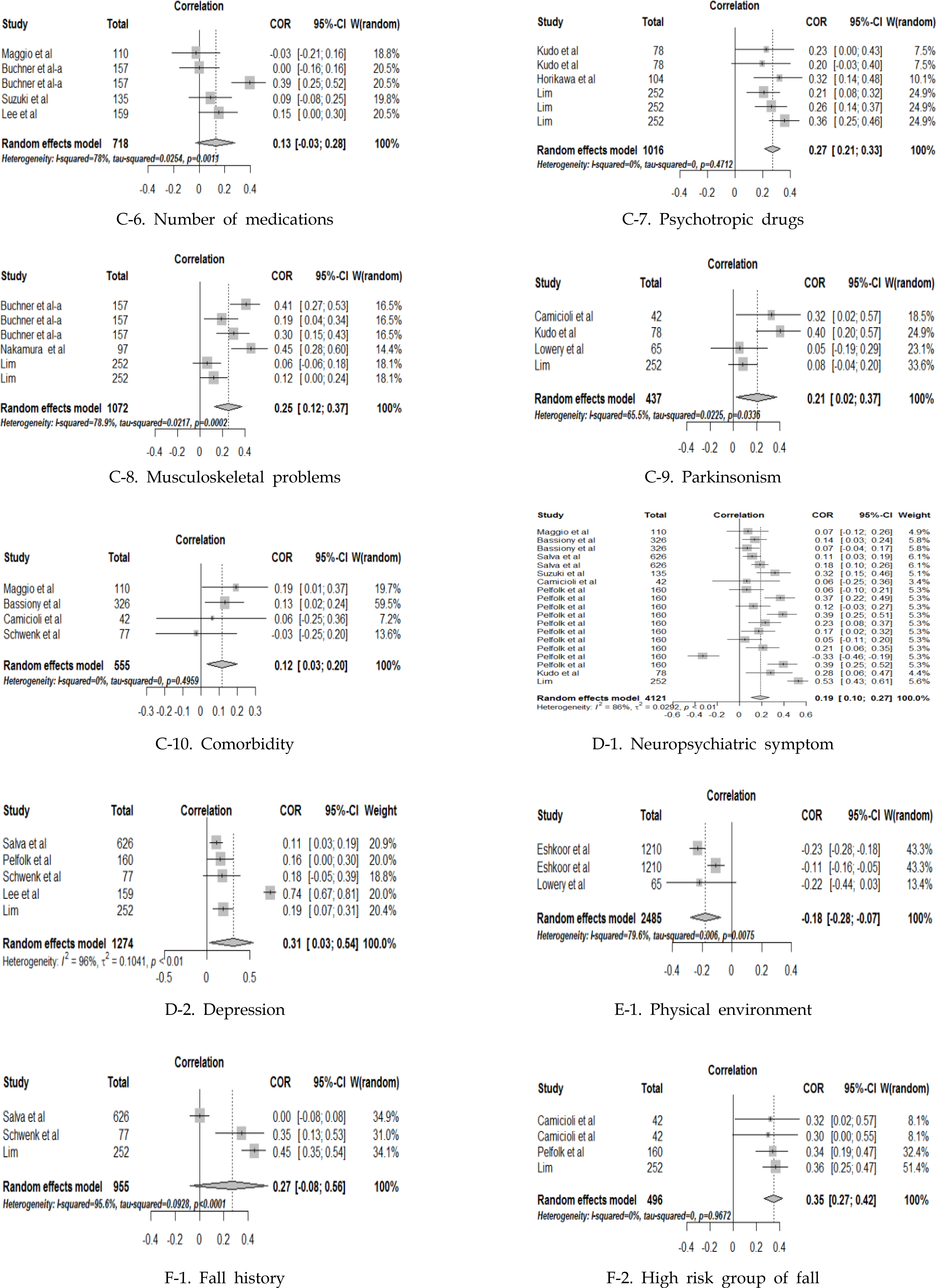
Characteristics of Studies Included in Meta-analysis
| Author (year) | Publication | Sample size | Setting | Risk factors | Quality assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buchner et al-a (1987) | Journal | 157 | Community | Balance, Number of medications, Musculoskeletal problems | 10 |
| Buchner et al-b (1988) | Journal | 157 | Community | Cognition | 9 |
| Nakamura et al (1996) | Journal | 97 | Nursing home | Age, Disease duration, Cognition, Walking, Musculoskeletal problems | 8 |
| Kanemura et al (2000) | Journal | 110 | Long term facility | Age, Cognition | 9 |
| Lowery et al (2000) | Journal | 65 | Community & Nursing home | Parkinsonism, Physical environment | 9 |
| Chung et al (2001) | Journal | 182 | Nursing home | Age, Gender, Cognition, ADL | 8 |
| Bassiony et al (2004) | Journal | 326 | Community | Age, Cognition, Comorbidity, Neuropsychiatric symptom | 9 |
| Camicioli et al (2004) | Journal | 42 | Long term facility | Age, Cognition, Walking, ADL, Parkinsonism, Comorbidity, Neuropsychiatric symptom, High risk group of fall | 9 |
| Horikawa et al (2005) | Journal | 104 | Outpatient clinic | Age, Gender, Cognition, BMI, Balance, Psychotropic drugs | 9 |
| Kudo et al (2009) | Journal | 78 | Community | Age, Gender, Disease duration, Cognition, Psychotropic drugs, Parkinsonism, Neuropsychiatric symptom | 9 |
| Pelfolk et al (2009) | Journal | 160 | Long term facility | Age, Cognition, Walking, ADL, Use of walking aids, Neuropsychiatric symptom, Depression, High risk group of fall | 10 |
| Maggio et al (2010) | Journal | 110 | Outpatient clinic | Age, Education, Cognition, BMI, ADL, Number of medications, Comorbidity, Neuropsychiatric symptom | 8 |
| Kato-Narita et al (2011) | Journal | 48 | Outpatient clinic | Cognition, Balance, ADL | 8 |
| Lee et al (2011) | Journal | 159 | Community | Age, Education, Cognition, Walking, Balance, ADL, Number of medications, Depression | 9 |
| Ryan et al (2011) | Journal | 43 | Community | Age, ADL, Use of walking aids | 9 |
| Salvà et al (2012) | Journal | 626 | Community | Age, Cognition, BMI, ADL, Neuropsychiatric symptom, Depression, Fall history | 10 |
| Suzuki et al (2012) | Journal | 135 | Long term facility | Cognition, ADL, Number of medications, Neuropsychiatric symptom | 8 |
| Schwenk et al (2014) | Journal | 77 | Long term facility | Age, Gender, Cognition, Walking, ADL, Balance, Comorbidity, Depression, Fall history | 9 |
| Eshkoor et al (2014) | Journal | 1210 | Community | Age, Gender, Education, Walking, Physical environment | 8 |
| Lim (2015) | Thesis | 252 | Long term facility | Age, Disease duration, Cognition, Walking, ADL, Use of walking aids, Psychotropic drugs, Musculoskeletal problems, Parkinsonism, Neuropsychiatric symptom, Depression, Fall history, High risk group of fall | 8 |
ADL=activity of daily living, BMI=body mass index.
ADL=activity of daily living, BMI=body mass index.