| Jaehee Jeon | 2 Articles |
Purpose
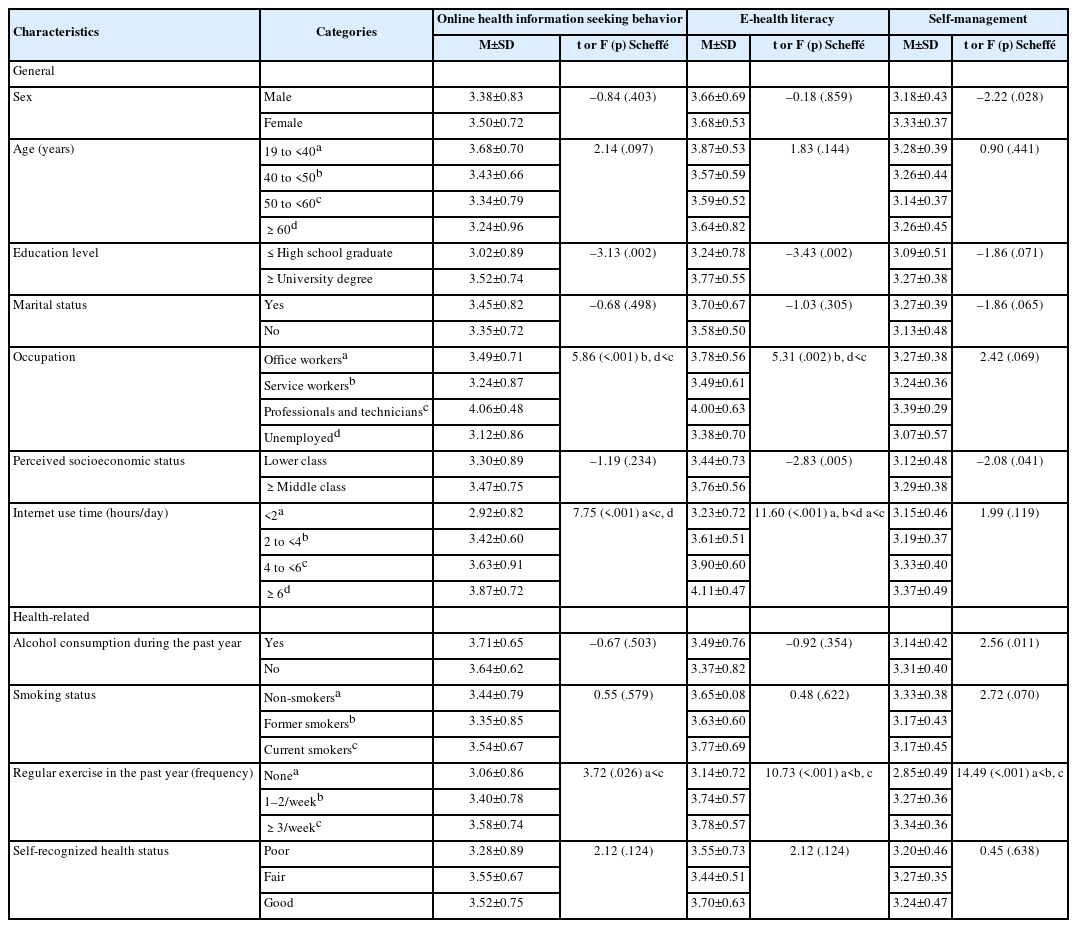
This study aimed to examine the influences of online health information-seeking behavior and e-health literacy on self-management among patients undergoing hemodialysis. Methods: A correlational survey was conducted with 150 adult hemodialysis patients who had been receiving dialysis for at least three months. Data were collected from July to November 2023 using structured questionnaires. The variables measured included online health information-seeking behavior, e-health literacy, and self-management. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, the independent t-test, one-way analysis of variance, Pearson correlation coefficients, and hierarchical multiple regression with IBM SPSS/WIN 28.0. Results: Participants demonstrated moderate to high levels of online health information-seeking behavior, e-health literacy, and self-management. Self-management was positively correlated with online health information-seeking behavior (r=.34, p<.001) and e-health literacy (r=.45, p<.001). Hierarchical multiple regression analysis identified e-health literacy (β=.30, p<.001), regular exercise during the past year (β=.27, p<.001), and alcohol consumption during the past year (β=−.22, p=.002) as significant predictors of self-management, explaining 32% of the variance. Conclusion: E-health literacy, regular exercise, and alcohol consumption significantly affect self-management among hemodialysis patients. Therefore, nursing interventions should focus on enhancing e-health literacy and promoting healthy lifestyle habits to strengthen self-management capabilities in this population.
Purpose
This study aimed to examine the relationship among professor-student interactions, grit, and adaptation to college life. Methods In this quantitative, cross-sectional study, participants completed a structured questionnaire comprising 48 items: 8 on general characteristics, 8 on professor-student interactions, 12 on grit, and 20 on adaptation to college life. Data were collected from 165 nursing students at two four-year universities between April 15 and May 20, 2023. Results Professor-student interactions had a mean score of 3.76±0.59 out of 5, grit had a mean score of 3.09±0.53, and adaptation to college life had a mean score of 3.48±0.51. Regression analysis identified significant predictors of adaptation to college life, including professor-student interactions (β=.26, p<.001), grit-perseverance of effort (β=.18, p=.047), and satisfaction with the major, with the "very satisfied" (β=.40, p<.001) and "satisfied" (β=.24, p=.002) categories showing significant impacts. The overall regression model was statistically significant (F=20.76, p<.001) and accounted for 32.5% of the variance in adaptation to college life. Conclusion Educational programs designed to strengthen professor-student interactions, enhance grit, and improve satisfaction with one's major should be developed to help nursing students adapt to college life. These findings have important implications for nursing education practices, the improvement of student support systems, and the preparation of students for their professional roles.
|
|

